ACCELERATE DISCOVERY
Rapidly identify and validate novel pain and CNS therapeutics
HUMAN INSIGHTS
Directly measure functional responses in human DRG, spinal cord tissues.
MECHANISTIC CLARITY
Uncover precise effects on ion channels and neuronal excitability
DE-RISK DEVELOPMENT
Predict clinical outcomes earlier with human data
ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY & CALCIUM IMAGING ASSAYS FOR DRUG DISCOVERY
AnaBios provides electrophysiology and calcium imaging assays to evaluate compound effects on human dorsal root ganglia (DRG) excitability. We utilize manual patch clamp to record neuronal action potentials or ionic currents. This technique offers precise measurement of action potential firing rate, action potential characteristics, rheobase and resting membrane potential.
AnaBios also provides fluorescence based calcium imaging to assess the effect of compound-receptor interactions. Combining calcium imaging with electrical field stimulation, we can evaluate the effect of compounds on neuronal excitability by measuring the calcium transients associated with action potential firing.
PAIN-RELATED FUNCTIONAL ASSAY DATA
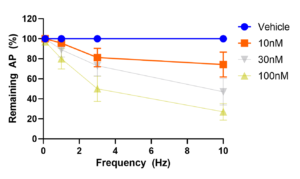
Figure 1 (below) plots the number of evoked action potentials at the pacing frequencies of 0.1Hz, 1Hz, 3Hz and 10Hz in 10 neurons that were exposed to two sodium channel antagonists, carbamazepine and PF-05089771.
Error bars are SEM. At 0.1Hz, the neurons are stimulated by a train of 10 current pulses. At 1Hz, 3Hz and 10Hz, the neurons are stimulated by a train of 120 current pulses at the respective frequencies. Both Carbamazepine and PF-05089771 inhibited action potentials in a concentration and frequency-dependent manner.
Figure 1: Carbamazepine Block of action potential firing
WHITE PAPER
ADVANCEMENTS IN NON-OPIOID PAIN MANAGEMENT THROUGH SELECTIVE NAV1.8 INHIBITION
This white paper explores the development of selective NaV1.8 sodium channel inhibitors as a promising non-opioid strategy for pain management. It details the molecular mechanisms of NaV1.8 inhibition, highlighting compounds such as suzetrigine (VX-548) and LTGO-33. By selectively blocking NaV1.8 in peripheral pain-sensing neurons, these inhibitors offer a novel approach to modulating pain signal transmission and reducing pain without the risks of opioid therapy.
Figure 2: Inhibition of TTX-R Currents in Human Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons by Known Nav1.8 Blockers
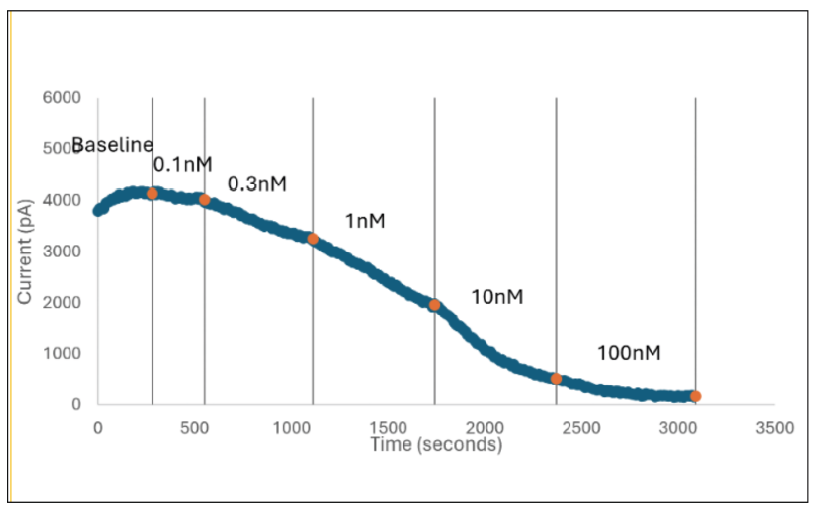
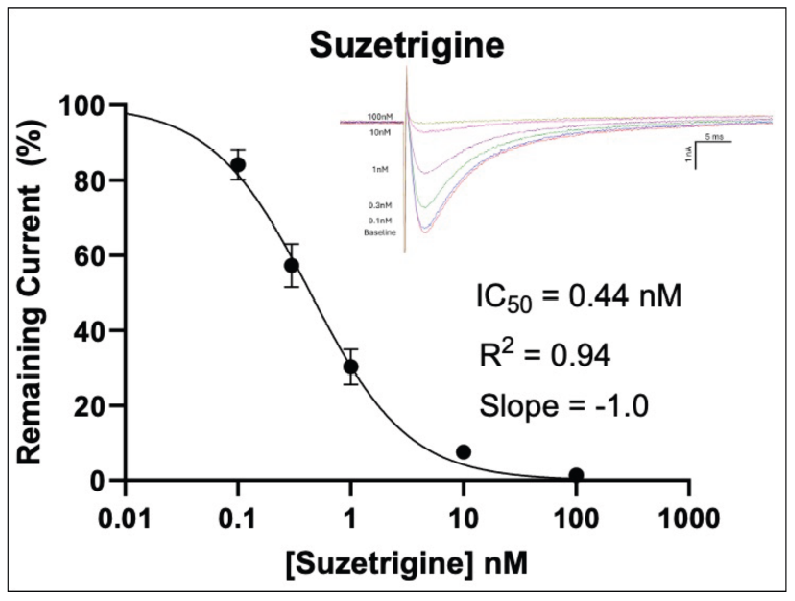
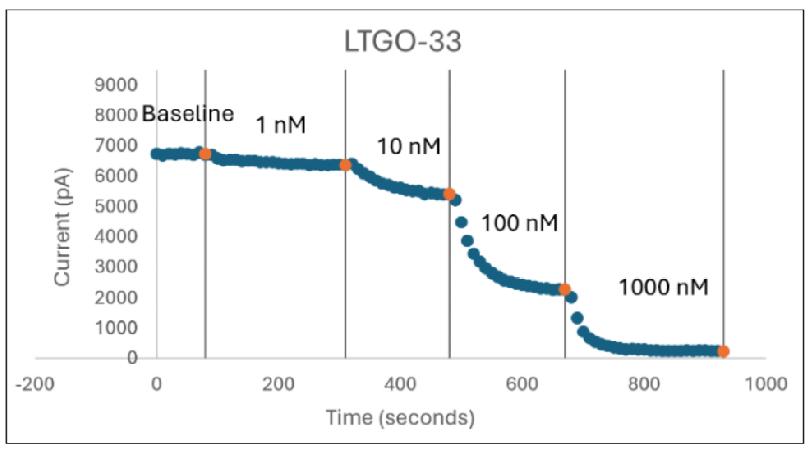
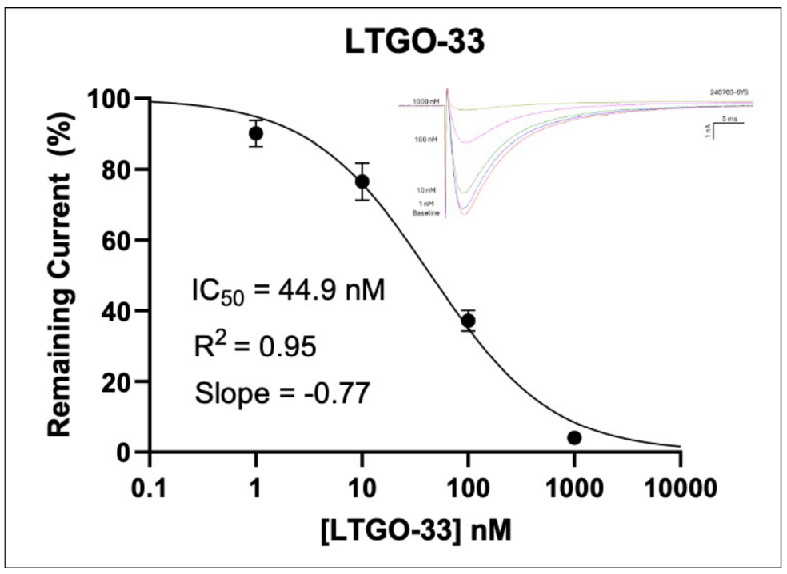
In Figure 2 (above), human donor DRGs were procured using AnaBios’ proprietary surgical techniques and shipped in a proprietary neuroplegic solution to AnaBios via dedicated couriers. The DRGs were then dissected in cold neuroplegic solution to remove all connective tissue and fat. The ganglia were enzymatically digested, and the isolated neurons put in culture.
Cells were plated on coated PDL-coated coverslips and recordings were made over the first 8 days-in-vitro. Currents were recorded with an Axon Instruments 700A amplifier and Clampex acquisition software. Signals were filtered at 3 kHz and sampled at 10 kHz. Currents were leak-subtracted using a P/-4 protocol. Sodium currents were elicited with a 50 ms voltage pulse to the peak of the I-V curve from a holding potential of -80mV. Inter-stimulus interval was 10 seconds.
Internal recording solution contained (in mM): CsF (135), MgCl2 (1), Na-ATP (2), EGTA (1), HEPES (10). External recording solution contained (in mM): NaCl (20), Choline-Cl (95), KCl (3), MgCl2 (1), CaCl2 (2), CdCl2 (0.1), NiCl2 (0.1), glucose (25), HEPES (10), TEA (20), TTX (0.0005). Both test agents were dissolved in DMSO (final DMSO concentration 0.1%).
Figure 3: Schematic of Calcium Transients Recording in
Human Dorsal Root Ganglia neuron
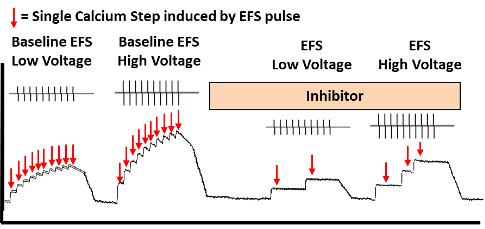
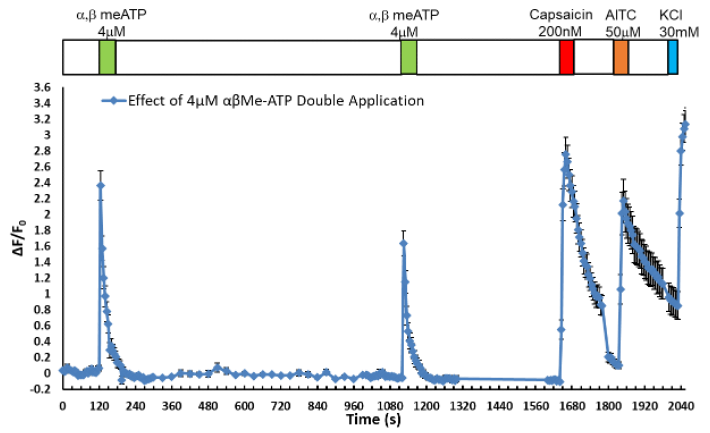
In Figure 3 (above) is a schematic figure of the recording of calcium transients (calcium steps) in a human DRG neuron loaded with Fluo-8 and stimulated by electrical field stimulation. The neural excitability in the form of evoked calcium steps can be measured simultaneously. The effect of a compound inhibitor can be measured by comparing the number of calcium steps pre and post addition of the inhibitor A.
Figure 3: Voltage Stimulation
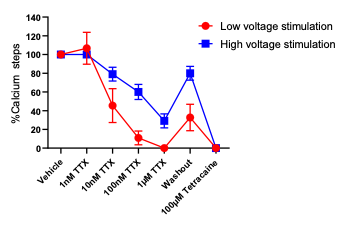
figure 4: activation of calcium transients

WHITE PAPER
Insights Into Fibrosis Pathways Using Human PCLS Models
This white paper introduces AnaBios’ innovative use of human precision-cut lung slices as a robust preclinical model for studying pulmonary fibrosis and testing anti-fibrotic therapies. It highlights the platform’s ability to retain human tissue architecture, providing physiologically relevant insights into disease mechanisms and therapeutic responses.
CURRENT CLAMP ASSAY – ACTION POTENTIAL FIRING
ASSAY FORMAT | DRUG CONCENTRATIONS | FREQUENCY | NUMBER OF CELLS |
|---|---|---|---|
Lead Candidate | 3 | 0.1, 1, 3, 10Hz | 10 |
Prostanglandin E2 + Bradykinin | 3 | 0.1, 1, 3, 10Hz | 10 |
Oxaliplain | 3 | 0.1, 1, 3, 10Hz | 10 |
Analysis includes rheobase, resting membrane potential, capacitance and number of action potentials at each frequency at each compound concentration.
RAMP CURRENT CLAMP ASSAY – ACTION POTENTIAL FIRING
ASSAY FORMAT | DRUG CONCENTRATIONS | NUMBER OF CELLS |
|---|---|---|
Lead Candidate | 3 | 10 |
Prostanglandin E2 + Bradykinin | 3 | 10 |
Oxaliplain | 3 | 10 |
Analysis includes rheobase, resting membrane potential, capacitance and number of action potentials for each applied ramp at each compound concentration.
VOLTAGE CURRENT CLAMP ASSAY – VOLTAGE-GATED SODIUM OR POTASSIUM CHANNELS
ASSAY FORMAT | DRUG CONCENTRATIONS | NUMBER OF CELLS |
|---|---|---|
Lead Candidate | 3 + hammer concentration | 5 |

HAVE MORE QUESTIONS?
CONTACT US
To inquire about products, services and pricing, please go to the ‘Contact Us’ page by clicking the button below.