About Us
It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when looking at its layout.

It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when looking at its layout.

Measures neuronal excitability & firing patterns
Generates data that better predicts clinical risk
Identifies neurotoxic liabilities using functional endpoints
Bridge the gap between preclinical research and clinical outcomes
The neurotoxicity of compounds on peripheral sensory neurons can be evaluated with human dorsal root ganglia (DRG) cultures at AnaBios. Clinical use of chemotherapeutic agents can be limited by the development of painful sensory neuropathy.
Dissociated human DRG neuronal culture can be used as an in-vitro model of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Multiple day treatment of human DRG neuronal cultures by oxaliplatin leads to neuronal death.
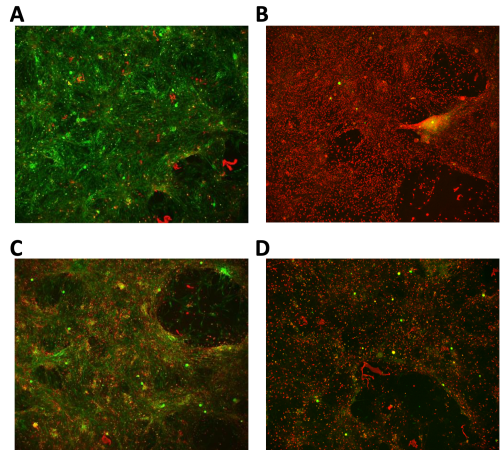
Figure 1 (above) shows a human DRG neuronal culture treated for 72 hours by vehicle (A), vehicle (B) followed by 0.1% saponin, 50µM oxaliplatin (C) and 500µM oxaiplatin (D). Viability and cell permeabilization were assayed by calcein (green) and ethidium homodimer (red) fluorescence.
AnaBios probes compound effects on spinal cord neuroexcitability through imaging of spontaneous calcium transients in organotypic slices from recovered human spinal cord. The effect of sodium channel inhibitors was evaluated by measuring the inhibition of action potential dependent calcium spikes in the spinal cord dorsal horn.
In Figure 2 (above), organotypic human spinal cord slice loaded with Fluo-8 exhibits spontaneous calcium activity in the dorsal horn. The figure shows spontaneous calcium transients in imaged individual neurons. Calcium traces from separate neurons are stacked along the y-axis. Application of escalating concentrations (3µM, 10µM, 30µM) of carbamazepine reduce the frequency of spontaneous calcium spikes. Tetrodotoxin at 1µM is applied at the end of the assay.

To inquire about products, services and pricing, please go to the ‘Contact Us’ page by clicking the button below.